In enterprise applications, nearly every request is executed within a database transaction.
Developers often use frameworks and libraries with declarative mechanisms to simplify transaction management.
The Spring framework, for example, uses a special annotation to arrange for method invocations to be automatically executed within a transaction. This annotation simplifies writing transactional business logic, making it easier to manage transactions in a monolithic application that accesses a single database.
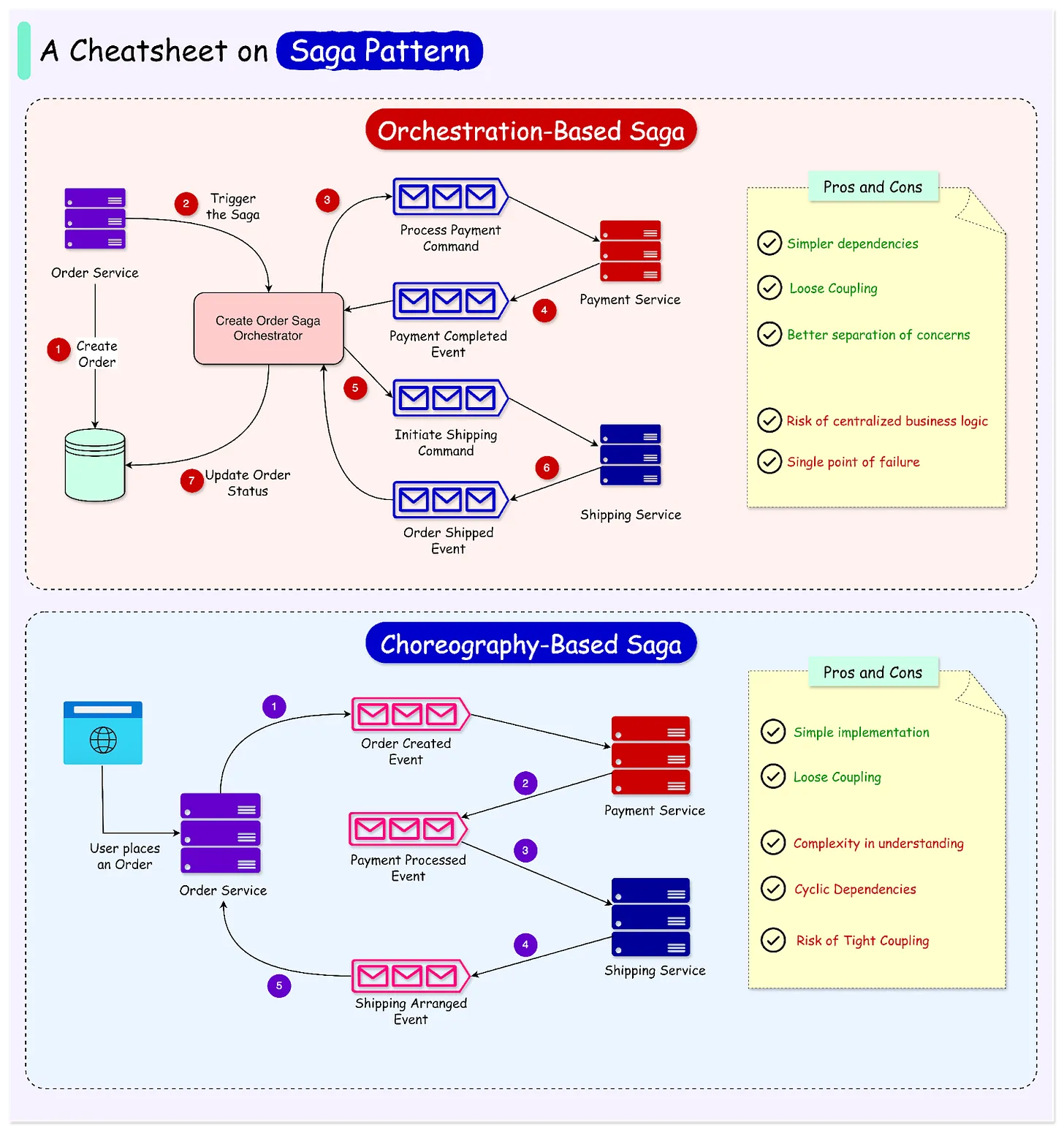
However, while transaction management is relatively straightforward in a monolithic application accessing a single database, it becomes more complex in scenarios involving multiple databases and message brokers.
For example, in a microservice architecture, business transactions span multiple services, each with its database. This complexity makes the traditional transaction approach impractical. Instead, microservices-based applications must adopt alternative mechanisms to manage transactions effectively.
You can find more in the below blogs